Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, presents one of the most daunting challenges in modern medicine. As researchers delve deeper into its complexities, the role of genetics emerges as a pivotal factor in both understanding its development and devising potential intervention strategies. This essay explores the intricate interplay between genetics and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, shedding light on how genetic factors influence susceptibility, progression, and potential treatment avenues. Moreover, it examines the promising role of cerebrolysin injection as a therapeutic intervention in mitigating the impact of genetic predisposition.
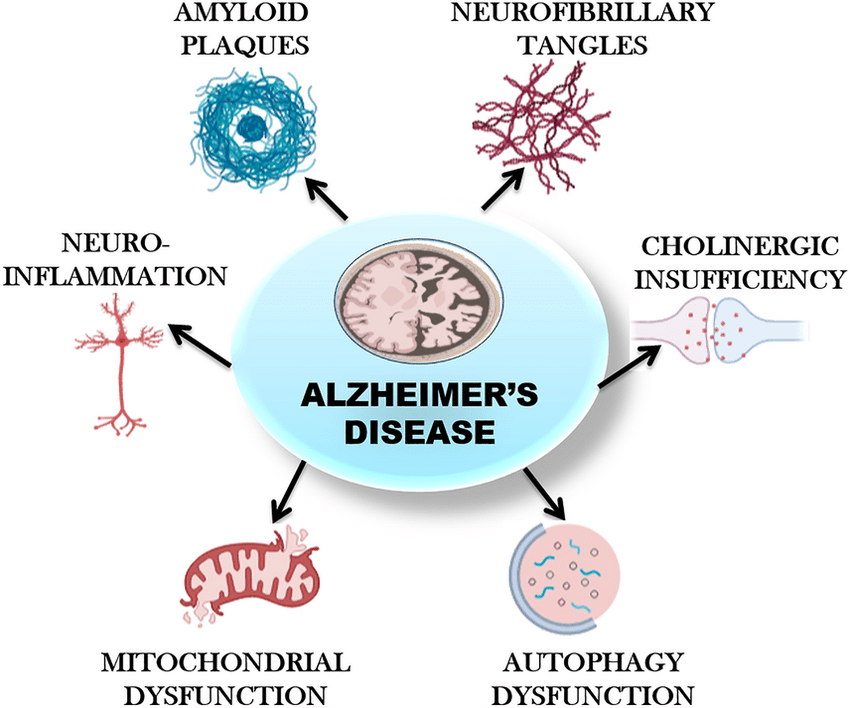
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, leading to cognitive decline and memory loss. While age remains the most significant risk factor, genetics also play a crucial role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to the disease. Variations in genes such as APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 have been identified as familial risk factors, contributing to early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, the apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene, particularly the 4 allele, has been strongly associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, influencing both disease onset and progression.
The discovery of these genetic links has provided invaluable insights into the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease. For instance, mutations in the APP gene influence the production and aggregation of amyloid-beta peptides, accelerating plaque formation. Similarly, mutations in presenilin genes disrupt intracellular signaling pathways, exacerbating neuronal dysfunction and death. Understanding these genetic mechanisms not only enhances our comprehension of disease pathogenesis but also paves the way for targeted therapeutic approaches.
In recent years, the concept of precision medicine has gained traction in Alzheimer’s research, aiming to tailor treatments based on individual genetic profiles. Cerebrolysin, a peptide-based drug derived from porcine brain tissue, has emerged as a promising candidate in this endeavor. Cerebrolysin exhibits neuroprotective and neurotrophic properties, promoting neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter regulation. Moreover, its ability to modulate neuro inflammatory processes makes it an attractive therapeutic option for Alzheimer’s disease, where neuro inflammation plays a significant role in disease progression.
Several studies have investigated the efficacy of cerebrolysin in Alzheimer’s disease, particularly in individuals with genetic predispositions. Clinical trials have demonstrated improvements in cognitive function, daily living activities, and global clinical status following cerebrolysin treatment. Importantly, these benefits appear to be more pronounced in patients carrying the APOE ε4 allele, suggesting that cerebrolysin may exert its effects through genetic modulation. By targeting specific genetic pathways implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrolysin holds promise as a personalized therapeutic intervention tailored to individual genetic profiles.
However, while the role of genetics in Alzheimer’s disease is undeniable, its influence is multifaceted and interacts with various environmental and lifestyle factors. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation, can modulate gene expression patterns, contributing to disease heterogeneity. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and social engagement can modify genetic risk, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to Alzheimer’s prevention and treatment.
In conclusion, genetics play a pivotal role in the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease, shaping individual susceptibility and response to treatment. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of the disease not only enhances our knowledge of its pathogenesis but also informs the development of targeted therapeutic strategies. Cerebrolysin, with its neuroprotective properties and potential for genetic modulation, represents a promising avenue for personalized intervention in Alzheimer’s disease. By unraveling the genetic threads of Alzheimer’s, we move closer to unraveling the complexities of this devastating condition and offering hope to millions affected worldwide.
Visit medicationplace site for more updates.